I just read, thank to a post by my friend Pat Folsom, that Great Grey Owls are back in the Montreal area for the first time in eight years. She pointed out a blog post by Chickaddd which I excerpt below:
One of the great things about winter birding is that every year is different and you never quite know how far south different species of birds will travel in search of food. Summer species are mostly predictable, as species typically return to the same nesting habitat each year since each species has fairly specific requirements for nesting. Finding a good place to nest requires the right type of vegetation, a good source of high-protein food for nestlings, and protection from predators. But in winter each species is only focused on one thing–finding enough food to survive the winter so that it can breed again next year. The availability of food changes each winter based on the cycles of temperature and precipitation, and thus determines how far a bird may have to migrate to find these food sources. Most of our insectivorous species have to travel to tropical climates where insects are available year-round, but frugivores (fruit-eating birds), granivores (seed-eating birds), carnivores, and omnivores can usually find year-round food sources in or near their breeding habitat and won’t migrate south unless conditions such as drought or extreme cold diminish their food sources. When food becomes scarce non-migratory species will slowly move their range south in search of a reliable food source. For some species, such as Redpolls, this happens regularly, on a fairly predictable 2-3 year cycle, but for other species the cycles are much less predictable, and may only happen every 5-10 years. One such species is the Great Gray Owl, which relies mostly on voles and other small rodents to get through the winter. Rodents are prolific breeders, so they tend to be abundant year-round, but occasionally the lack of food will cause rodent populations to crash, forcing the Great Gray Owl out of its northern boreal forest habitat and into areas where rodents are still abundant. Surprisingly one of the best places for an owl to find a good supply of rodents this time of year is the bustling metropolis of Montreal.
About a month ago reports of Great Gray Owls throughout Quebec started appearing on birding list-serves, mostly from urban parks that are in and around Montreal. Great Gray Owls need open fields to hunt, and mature trees to hunt from, which many of Montreal’s parks provide. The last Great Gray Owl invasion was eight years ago, in 2005, when there were dozens of them across the city. The greatest concentration of them was on Ile Bizard, an island on the northwest side of Montreal, that has a large nature park surrounded by suburban housing–perfect rodent habitat. In 2005 I had just moved to Plattsburgh, only an hour from Montreal, and so I made the trip up there to see the owl invasion. It was an incredible experience, Great Gray Owls seemed to be everywhere, I saw at least half a dozen that day. Even more amazing was how close you could get to them, you could practically walk right underneath them and they still wouldn’t leave their perch. Being such a large bird, 70-80cm in length and a wingspan up to 152cm, they don’t take flight unless absolutely necessary due to the energy involved, so they just stay perched most of the day. Since they aren’t hunted and have few natural predators they don’t seem to feel threatened by humans, they simply stare at you as you walk by with their gorgeous yellow eyes. Then they look quickly look away and return to what they were doing before you disturbed them–using their incredible senses to listen for food. Though owls have excellent eyesight it is near impossible to spot a rodent in snow-covered fields so they rely on sound instead to find rodents burrowing beneath the snow.The disk-like appearance of a Great-Gray Owls face serves a purpose–the arrangement of the feathers funnels sound into the owl’s ears, making its hearing keen enough to hear a vole tunneling beneath a foot of snow. When they hear a vole they take to the air with very slow stiff wingbeats and then glide silently over the field so that they can use their ears to pinpoint the vole’s exact location before it plunges into the snow to capture its prey. Their silent flight has earned them the nickname “Ghost Owl”, because they glide like a ghost over the field, undetectable by their prey.
Such a cool creature is certainly worth making a second trip to Montreal to see, eight years later, so this past weekend I assembled a car full of birders to ride with me across the border in search of one of these amazing birds, two of which had never seen a Great Gray Owl before… (read whole post)
I checked eBird for listings with no success on recent sightings but, as you will read in Chickaddd’s post, many are concerned about reporting Great Grays because of the actions of over-eager photographers who bait and bother owls for better photos.
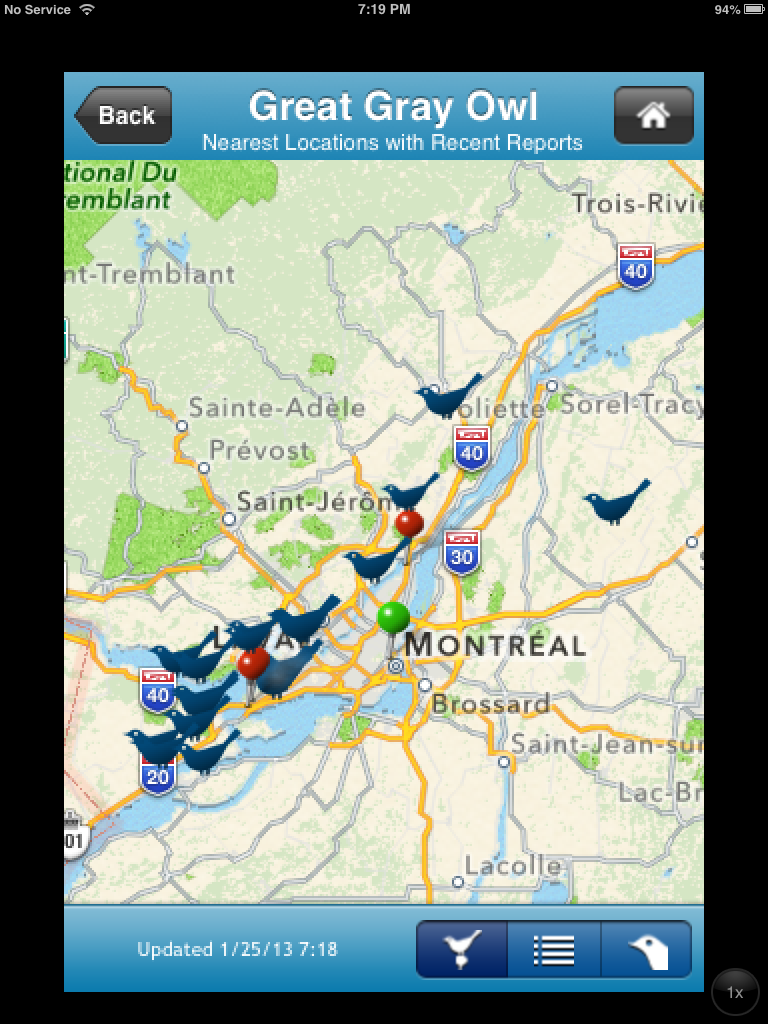
Most of these sightings are two or three weeks old. Chickaddd and friends report where they saw one last weekend.
Discover more from Vermont Birder
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


Pingback: Great Gray Owl in Hanover, NH